zMAP - Proteomics Analysis Platform
zMAP, a new computational framework developed for simultaneously comparing multiple proteomic profiles and downstream functional analysis of detected protein expression changes.
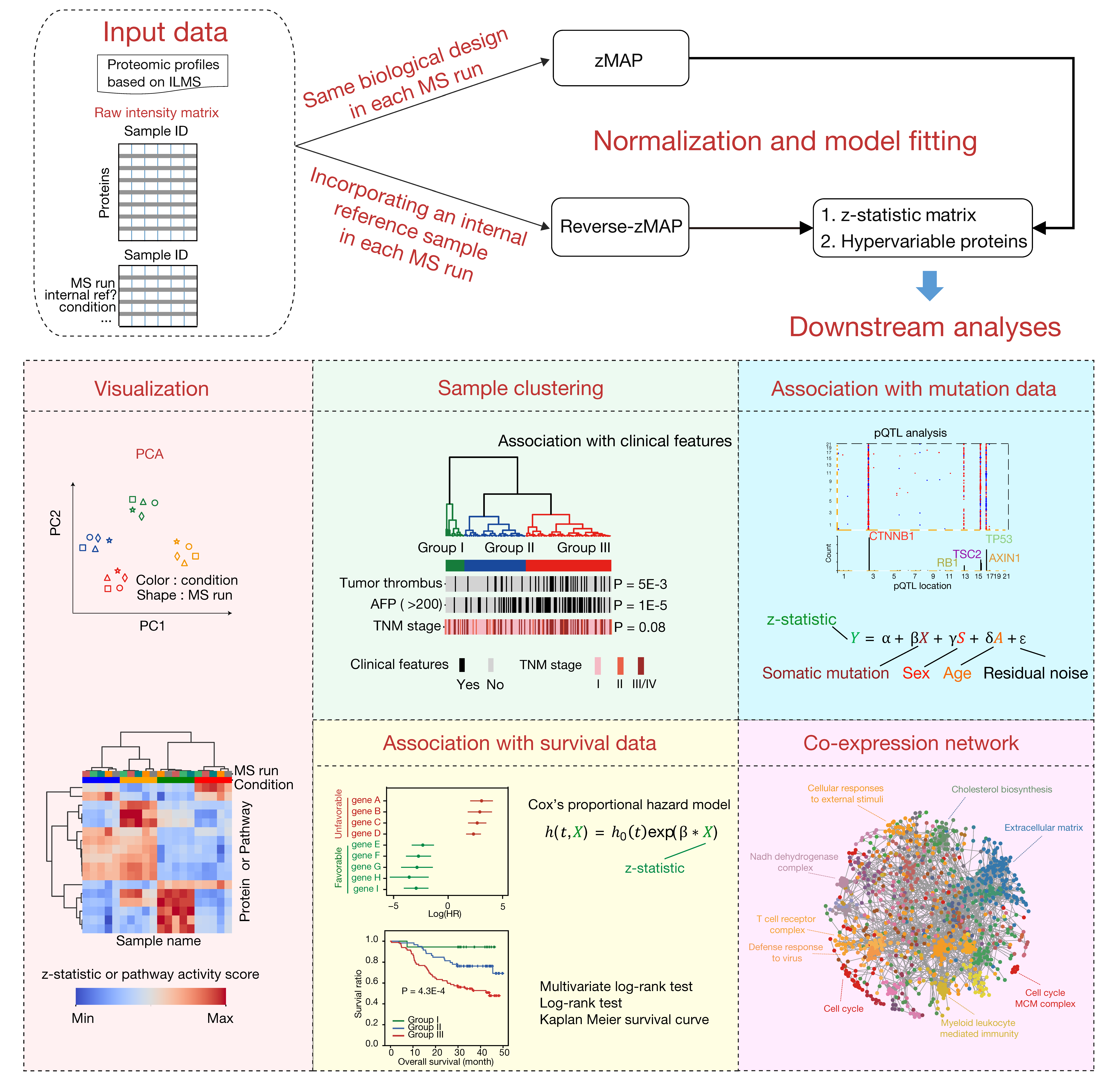
Isobaric labeling-based mass spectrometry (ILMS) has been widely used to quantify, on a proteome-wide scale, the relative protein abundance in different biological conditions. Large-scale proteomic studies based on ILMS, however, typically involve multiple runs of mass spectrometry (MS), bringing great computational difficulty to the simultaneous comparison and other integration analyses of all ILMS samples.
We present zMAP, a toolset that makes ILMS intensities comparable across MS runs by modeling the associated mean-variance dependence and accordingly applying a variance stabilizing z-transformation. Specific efforts have been made to render the model fitting procedure resistant to underlying hypervariable proteins. Two case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of zMAP in handling large-scale ILMS data sets. Specifically, the transformed z-statistics, as a new kind of measurements of protein abundance, have effectively unlocked a broad range of integration analyses that cannot otherwise be applied on original ILMS intensities.
Query your existed process id